News broadcast | Perception of ecological change-Mother River reappears vitality and vigor
The Yangtze River and the Yellow River are the mother rivers of the Chinese nation, which have nurtured a long history of Chinese civilization. General Secretary of the Supreme Leader emphasized that "the Yangtze River and Yellow River basins are the main battlefields of ecological civilization construction". Since the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China, through a series of important measures, remarkable achievements have been made in the ecological protection and management of the Yangtze River and the Yellow River, and the mother river has regained its vitality.
The main stream of the Yangtze River has maintained Grade II water quality for five consecutive years.
On the banks of Liangzi Lake in Ezhou, Hubei Province in the Yangtze River Basin, as night falls, millions of fireflies attract an endless stream of tourists.
The team led by Fu Xinhua has been monitoring the migration and survival of fireflies for 20 consecutive years.

Fu Xinhua, a professor at Huazhong Agricultural University: In the past five years, the population size of rare aquatic fireflies has been expanding at a rate of 15% to 20% every year. Because these aquatic fireflies can only live in Class I water, it can also directly reflect that our water environment is getting better.

The research team’s high-sensitivity monitor and AI tracking and identification technology recorded the "footprints" of more than ten aquatic fireflies in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River: since 2016, the population size of the aquatic fireflies, which is the most sensitive to the water environment, has continued to expand. In ten years, the number has increased by more than 10 times.
In the air of 10,000 meters high, remote sensing satellites also perceive the ten-year changes in the water quality of the Yangtze River around fireflies.

This is a remote sensing satellite image taken in April 2015 in a tributary of the Changjiang River in Xianning, Hubei Province. The darker the yellow color, the higher the concentration of total phosphorus in the main pollutant.

This is the image of the same river section in April this year, and the color has changed from yellow to green, indicating that the total phosphorus concentration has dropped significantly.
In the past ten years, nearly 10,000 chemical enterprises in the Yangtze River Basin have been shut down and moved. While the pollution sources are decreasing, the "Skynet" that supervises the sewage outlets is becoming more and more dense.

By the end of 2024, the Yangtze River Economic Belt had surveyed 140,000 kilometers of river and lake shoreline, and found more than 180,000 sewage outlets into the river, with a remediation completion rate of about 90%.
According to the latest data, the water quality of the main stream of the Yangtze River has maintained Class II for five consecutive years.
The sediment discharge of the Yellow River in 2024 is more than the previous years’ average.
Reduce by over 80%
From the Yangtze River basin with dense water system to the north, the Yellow River, which is symbiotic with the Yangtze River, has also experienced ecological transformation in the past ten years.
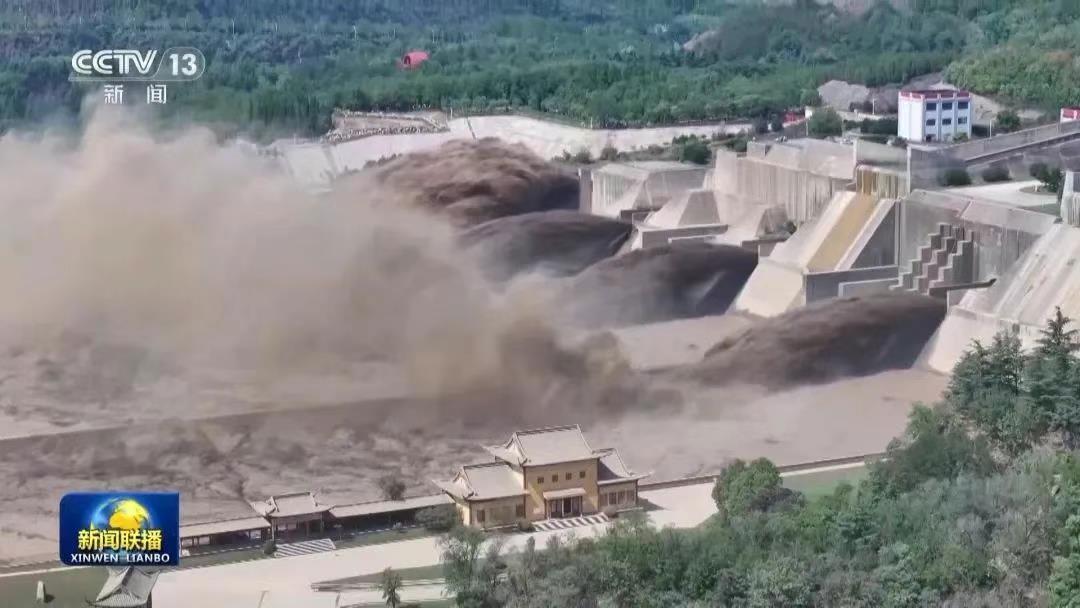

This summer, Wanjiazhai, Sanmenxia and Xiaolangdi water control projects in the middle reaches of the Yellow River jointly carried out the 30th water and sediment transfer operation.
At Tongguan Hydrological Station in the upper reaches of Xiaolangdi Reservoir, the on-line photoelectric sediment detector penetrates the Yellow River water with light and senses the change of sediment content. We found that the sediment content in every cubic meter of Yellow River water flowing here decreased from the average of 27.5 kg (1952-2020) to 5.76 kg in 2024.
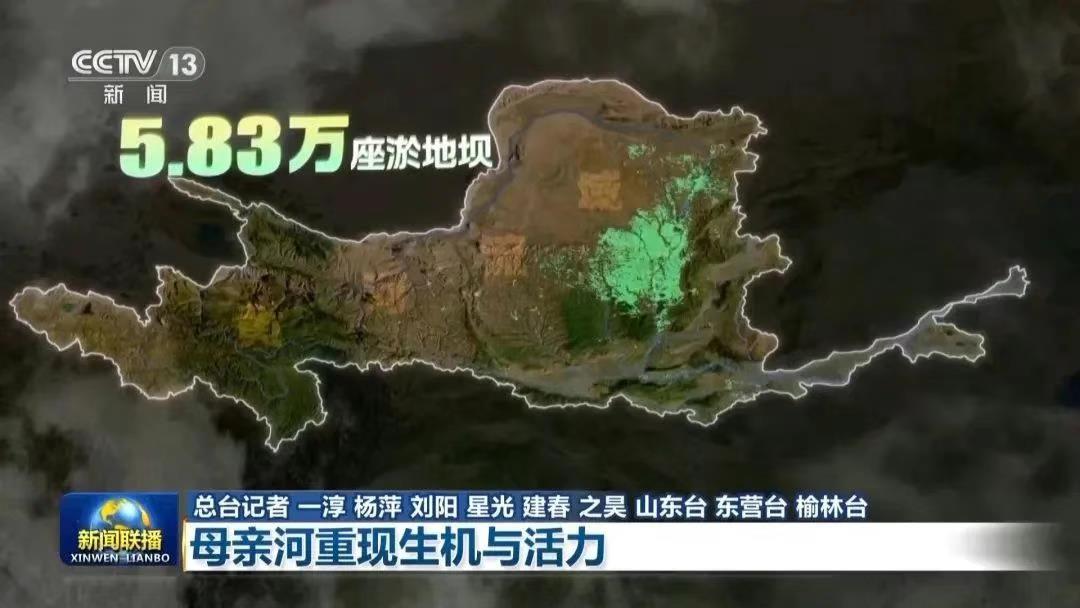
The key to the decrease of sediment in the Yellow River year by year lies in the Loess Plateau.
Overlooking the gullies on the Loess Plateau from high altitude, we saw a warping dam built to intercept floods and sediments. Today, there are 58,300 silt dams in the Yellow River Basin, with a cumulative sand retention of 7.4 billion tons. In 2024, the sediment discharge of the Yellow River decreased by over 80% compared with the previous years’ average.

When the satellite images of the Yangtze River estuary fade away from the turbidity of the past; When the Yellow River Delta is transformed into an ecological paradise where birds flock together, the rejuvenation of the Mother River not only allows the residents in the basin to share the ecological well-being, but also creates a "green backbone" for the sustainable development of the Chinese nation!